Secondary storage hash tables are much like main memory ones
Recall basics:
There are buckets
A hash function f(k) maps a key k to {0, 1, …, n-1}
Store in bucket f(k) a pointer to record with key k
Secondary storage: bucket = block, use overflow blocks when needed
Assume 1 bucket (block) stores 2 keys + pointers
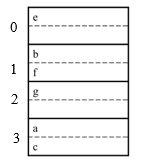
h(e)=0
h(b)=h(f)=1
h(g)=2
h(a)=h(c)=3
Search for a:
Compute h(a)=3
Read bucket 3
1 disk access
Insertion:
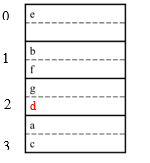
place in right bucket, if space
E.g. h(d)=2
Overflow blocks
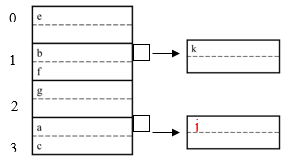
Create overflow block, if no space
E.g. h(k)=1
Performance
Excellent, if no overflow blocks
Degrades considerably when number of keys exceeds the number of buckets (I.e. many overflow blocks).
Extensible Hash Table:
Allows hash table to grow, to avoid performance degradation
Assume a hash function h that returns numbers in {0,…,2^k – 1}
Start with = 2^i≪2^k , only look at first i most significant bits 𝑖=1, 𝑛=2^𝑖, 𝑘=4 bit int (or whatever)
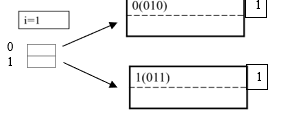
Note – we only look at the first bit.
Insert 1010
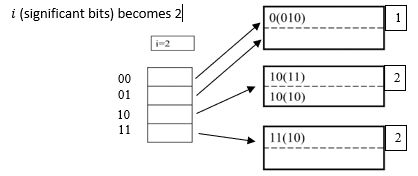
Need to extend table, split blocks:
Noww insert 0000,
then 0101
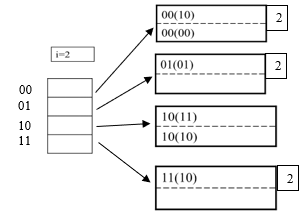
What if we
inserted 0001?
This would
“extend” the hashtable again i=3
Extensible Hash Tables performance
No overflow blocks: access always one read
BUT:
Extensions can be costly and disruptive (Power of 2)